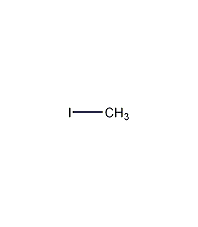
Structural formula
| Business number | 01HL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3I |
| Molecular weight | 141.94 |
| label |
Methyl iodide, Monoiodomethane, Methyl iodide, methylation reagents, Extinguishing agent, Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents |
Numbering system
CAS number:74-88-4
MDL number:MFCD00001073
EINECS number:200-819-5
RTECS number:PA9450000
BRN number:969135
PubChem number:24857202
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with a special odor. Turns brown when exposed to light. [12]
2. Melting point (℃): -66.5[13]
3. Boiling point (℃): 42.5[14]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 2.3[15]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.89[16]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 50 (20℃)[17]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -813.8[18]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 254.8[19]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.36[20]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.51~1.69[21]
11. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. [22]
12. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.5270
13. Eccentricity factor: 0.193
14. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.172
15. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 4.600×109
16. van der Waals volume (cm3 ·mol-1): 32.850
17. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 14.7
18. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 253.81
19. Gas phase standard Free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 16.4
20. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K -1): 44.08
21. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -12.3
22. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 162.8
23. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ ·mol-1): 16.5
24. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):82.91
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[23]
LD50: 100~200mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 1300mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[24] Human Transdermal: 1g (30min), mild irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [25] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 2μl/dish; Escherichia coli 20μmol/L. Mammalian somatic cell mutagenesis: mouse lymphocytes 15mg/L (2h). DNA damage: E. coli 1μmol/L.
4. Carcinogenicity [26] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[27]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 168~672
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 672~2688
3. Non-biodegradability[28]
Maximum light absorption of photolysis (nm): 260
Photooxidation half-life in water (h): 480~1440
The half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 535~5348
The half-life of primary hydrolysis (h): 2640
4. Other harmful effects [29] This substance is harmful to the environment and attention should be paid to atmospheric pollution.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 19.65
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 63.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 145.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 27.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 7.79
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 2
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Methyl iodide is toxic, corrosive and may cause cancer. It should be placed in a brown bottle during storage to prevent the release of I2 when exposed to light. In addition, the storage temperature should be low.
2. Stability[30] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[31] Strong oxidants, strong alkali, silver chlorite, sodium, magnesium, zinc, etc.
4. Polymerization hazards[32] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[33] Hydrogen iodide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[34] Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the disproportionation of dimethyl sulfate:
![]()
2. Mix potassium iodide, water and a small amount of calcium carbonate evenly under stirring, heat to 60-65°C and keep warm, then slowly add the theoretical amount of dimethyl sulfate dropwise, and after the addition is completed, lower the temperature. Rise to 65~70℃, and methyl iodide evaporates during the reaction:
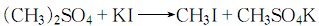
The evaporated liquid is allowed to stand and then separated into layers. The water layer is discarded. After the oil layer is dried and dehydrated with anhydrous calcium chloride, a small amount of potassium iodide particles are added for distillation. The 41-43°C fraction is collected, which is the finished product. .
3. Add red phosphorus and methanol to tank A, add iodine tablets to tank A, heat tank A with steam, so that the methanol boils and evaporates into tank A, contacts the iodine tablets and flows back to tank A. , repeat until the solution is nearly colorless. Then it is evaporated to obtain crude methyl iodide. The heating speed should be controlled during the process to prevent the reaction from being too intense. The reaction formula is:
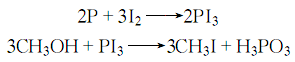
Crude iodine The methane is washed once with water, 5% sodium carbonate and 5% sodium thiosulfate in sequence to obtain a colorless liquid, which is left to separate into layers. Remove the lower liquid and use anhydrous calcium chloride, a small amount of sea wave, and dry sodium carbonate to seal and dry in the dark. , and then filtered to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. This product is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of iodomethylmethionine (vitamin U), analgesics, antidote phosphonate and other drugs; in organic synthesis It is used as a methylating agent to synthesize iodoform; in addition, it is also used as a fire extinguishing agent.
2. Methyl iodide can be used to methylate carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and trivalent phosphorus.
C-methylation Methyl iodide is an active alkylating reagent that can be used with ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amino compounds, Carbanions formed by cyano compounds, nitroalkanes, sulfones, sulfoxides, imines and hydrazones act to carry out methylation reactions. In the reaction, the amount of methyl iodide used varies greatly, sometimes in a small amount, and sometimes it can even be used as a solvent.
Under the action of a strong base (such as n-butyllithium), the carbon atom at the α- position of the carbonyl group can be methylated (Formula 1) [1].
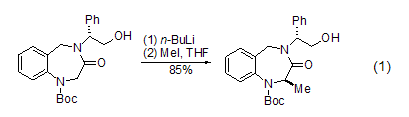
O -Methylation In DMF solution, carboxylic acid reacts with iodine in the presence of a base such as potassium carbonate, potassium bicarbonate or diisopropylethylamine [2] Methane reaction to prepare the correspondingester. Phenolic hydroxyl groups can often also be methylated under such conditions[3], while fatty alcohol methylation usually occurs in aprotic polar solvents using stronger bases (Formula 2) [4].
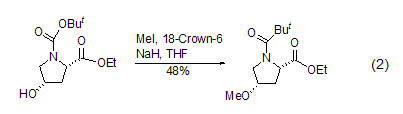
S -Methylation Methyl iodide can methylate sulfides such as thiols [5] to obtain sulfides and sulfonium salts. For example, the reaction between thioamide and methyl iodide in THF can methylate thio to form thioether (formula 3)[6].
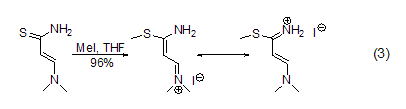
N -Methylation Methylation of ammonia and primary amines with methyl iodide is generally not a good method because further methylation will occur, but for secondary and tertiary amines Methylation is a better method and can be used to prepare tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salts[7]. In acetonitrile solvent, tritylamine is methylated with methyl iodide to obtain the product with higher yield (Formula 4)[8]. The nitrogen atoms in the heterocyclic ring can also be methylated with methyl iodide (Formula 5)[9,10].
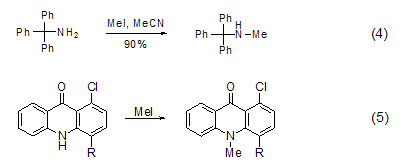
P -Methylation The reaction between three-coordinated phosphorus and methyl iodide can generate salt (formula 6) [11]. Usually, this reaction occurs in polar solvents such as acetonitrile, Perform in DMF or THF.
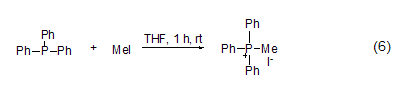
3. Used in medicine, organic Synthesis, testing of pyridine, microscopy, etc. [35]
extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/high-quality-nn-dicyclohexylmethylamine-cas-7560-83-0/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-ne210-balance-catalyst-ne210-dabco-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nn-dicyclohexylmethylamine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-ef-350-low-odor-balanced-tertiary-amine-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/jeffcat-dmea-catalyst-cas107-15-3-huntsman/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dimethylbis1-oxoneodecyloxystannane/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44169extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-lc-5630-thermosensitive-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/2-dimorpholinodiethylether/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/u-cat-1102-catalyst-cas135176-05-4-sanyo-japan/


